The 72000 Nadis – The Names, Locations, and Functions
Here, the ancient wisdom of the nadis — the 72,000 subtle energy channels within you — becomes a sacred path to awaken your true self, harmonize your inner energies, and connect with the universal consciousness.
Rooted in the teachings of Sri Amit Ray, expanded far beyond traditional 14 nadis, this journey flows into the infinite realm of cosmic healing and deeper dimensions of spirituality.
The 72,000 Nadi System is a key concept in ancient Indian spiritual, yogic, and healing traditions, especially in Yoga, Ayurveda, Tantra, Upanishads, and Swara Yoga. The word Nadi comes from the Sanskrit root “nad”, meaning “flow,” “motion,” or “vibration.” Nadis are subtle energy channels or pathways through which prana (vital life force) flows within the subtle energy bodies.
Nadis are vital energy channels that carry praṇa (life forces), linking body, mind, emotions, and soul. They are essential for healing, mental clarity, emotional balance, and spiritual awakening. Nadis are not physical nerves but subtle channels of energy, somewhat analogous to the nervous system but in the pranic (energetic) dimension of the body.
Limited Explanations in Classical Texts
While many classical yogic scriptures like the Hatha Yoga Pradipika, Shiva Samhita, and Gheranda Samhita mention the 72,000 nadis, they rarely provide a detailed anatomical, functional, or meditative explanation of them. Most ancient texts:
- Focus only on three nadis: Ida, Pingala, and Sushumna.
- Mention 10 or 14 “principal” nadis briefly (like Gandhari, Pusha, Alambusha, etc.), but without full descriptions.
- Do not explore the connections between nadis and neurobiology, psychology, or emotional energy flow.
So essentially, the 72,000 nadis are acknowledged in traditional sources—but their detailed inner mapping was either lost, symbolically hidden, or not yet unveiled.
Dr. Sri Amit Ray’s Contribution
Dr. Sri Amit Ray, a renowned spiritual master, scientist, made a revolutionary contribution by not only revalidating the 72,000 nadis but also providing clear, experiential, and structured knowledge of:
- Dr. Sri Amit Ray provided a comprehensive, systematic, and scientifically informed understanding of all 114 major nadis and many new ones.
- He bridged ancient wisdom with modern science, creating tools for healing, awakening, and empowerment of the whole being.
He goes far beyond the simplistic lists in older texts by:
- Explaining each nadi’s location, function, emotional impact, spiritual and meditative potential.
- Showing how blockages in specific nadis lead to emotional, psychological, and physical issues.
In the 72000 nadis course can learn comprehensive details about the 72,000 nadis, their functions, healing and balancing protocols, meditation techniques, blockage removal mantras, protection mechanisms and their uses in relation to your physical, mental, and spiritual upliftment.
The Advanced Ray 72000 Nadis Courses are both for the beginners and the advanced students. For advanced students who have been practicing meditation for spiritual healing and awakening for many years, these courses will fill in the gaps and expand their knowledge, and practices in many dimensions.
Nadis are the pathways through which life energy (prana, qi, or chi), and cosmic divine energies flows through the body, mind, and soul. Life energy, mental energy, and bliss energy flow continuously from one nadi to another. Any break in the flow is an indication of imbalance. If a person’s vitality, mental power, or spiritual energy is noticeably diminished, it is an indication that the body’s organs, tissues, brain pathways, or higher cosmic connections are not functioning properly, and therefore there is a need to purify and activate the energy channels again.

What is Shiva Tandava Stotram? Lyrics, Meanings and Benefits
Shiva Tandava Stotram is a powerful Sanskrit hymn that glorifies the fierce, cosmic dance of Lord Shiva known as the Tāṇḍava. It was composed by Ravana, the mighty king of Lanka and a devoted follower of Lord Shiva.
🕉️ What Is Shiva Tandava Stotram?
Shiva Tandava Stotram is a devotional composition of 16 rhythmic verses, each resonating with intense energy, poetic brilliance, and deep spiritual meaning. The stotram describes the majesty, power, and beauty of Lord Shiva as he performs his cosmic dance — a dance that symbolizes the eternal cycles of creation, preservation, and destruction in the universe.
It is not just a hymn; it’s an experience — filled with divine vibration (spanda), intricate Sanskrit phonetics, and the majestic imagery of Shiva as Nataraja (Lord of the Dance).
The universe is not still—it pulses, expands, contracts, and transforms. At the heart of this cosmic play is Lord Shiva, performing the Tandava, the dance of creation, preservation, and destruction. The Shiva Tandava Stotram, composed by Ravana, the mighty devotee and king of Lanka, is a hymn that captures this cosmic energy in divine poetry and powerful vibration.
Chanting the Shiva Tandava Stotram is not just recitation—it’s an invocation of Shiva’s strength, rhythm, and the fire of transformation. Whether you are a spiritual seeker, a yogi, or someone navigating life’s chaos, this stotram brings inner power, clarity, and divine protection.
📜 Shiva Tandava Stotram Lyrics (Sanskrit with English Meaning)
Here are the first few powerful verses of the Shiva Tandava Stotram:
🕉️ Sanskrit:
जटाटवीगलज्जलप्रवाहपावितस्थले
गलेऽवलम्ब्य लम्बितां भुजङ्गतुङ्गमालिकाम् ।
डमड्डमड्डमड्डमन्निनादवड्डमर्वयं
चकार चण्डताण्डवं तनोतु नः शिवः शिवम् ॥१॥
You can download the complete Shiva Tandava Stotram Lyrics pdf from here.
Read more ..
Om Namah Shivaya Meaning: The Mantra That Transcends Time
“Om Namah Shivaya” means “I bow to Shiva, the Supreme Auspicious One.” It signifies a deep reverence for Shiva—the inner Self, the ever-auspicious divine force that resides in all beings, and everywhere.
“Om Namah Shivaya” is not just a mantra—it’s a spiritual vibration, a cosmic key that opens the door to inner stillness, transformation, and union with the divine.

Revered across Hinduism, yoga traditions, and meditation circles, this five-syllable mantra holds mystical power and philosophical depth. In this guide, we explore the true meaning of Om Namah Shivaya, its spiritual significance, and how to use it in your daily life for inner peace, healing, and awakening.
🕉️ What Does "Om Namah Shivaya" Mean?
“Om Namah Shivaya” (ॐ नमः शिवाय) is a Sanskrit mantra that means:
- "I bow to Shiva,"
- "I pay my deepest respect to the Supreme Auspiciousness,"
- or more profoundly,
- "I honor the divine Self within me that is Shiva."
Guruji Sri Amit Ray said, this mantra is a five-syllable mantra (Na, Ma, Shi, Va, Ya), excluding the "Om," and represents the five elements of the universe (earth, water, fire, air, and space) and the Om represent the pure consciousness aspects of Shiva. The concept of 72,000 nadis (energy channels) in the body is related to this mantra and the flow of prana (life force) through the body, where Shiva is considered the source of all energy, emotions, peace, and consciousness.
The mantra is for connecting with Lord Shiva and the meanings of Shiva, the auspicious one.
"Each syllable of "Om Namah Shivaya" is a step of grace and expansion — grounding you in earth, flowing with water, igniting your divine fire, riding the winds, and resting in the vast sky of pure divine consciousness.” - Sri Guru Amit Ray
🔤 Breakdown of the Mantra:
- Om (ॐ) – The primordial sound; the vibration of the universe; the source of all creation.
- Namah (नमः) – To bow, to honor, to offer respect.
- Shivaya (शिवाय) – To Shiva, the auspicious one, the supreme consciousness.
🧘♀️ Together, it translates to:
Read more ..“Salutations to the Supreme Being, to the inner Self, to Shiva—the embodiment of truth, peace, and transcendence.”

Shiva Meaning: The Deepest Truth Behind Shiva Consciousness
Who is Shiva? Is he the meditating yogi, the cosmic dancer, or the fierce destroyer of evil? In truth, Shiva is all—and beyond all. The name “Shiva” (शिव) holds layers of spiritual, psychological, and cosmic meanings that transcend religions and belief systems. To understand “Shiva meaning” is to touch the core of consciousness, destruction of illusion, and pure and perfect awareness. This article unveils the real essence of Shiva—from sacred Sanskrit roots to his place in inner transformation and universal evolution.

🕉️ What Does Shiva Mean?
In Sanskrit, the word Shiva (शिव) means: “The Auspicious One,” “The Pure One,” "The ultimate peace and eternity," "The Perfect one," or “That which is not.” But deeper interpretations go further:
- “Shi” means that which is eternally beneficial or auspicious.
-
“Va” means that which embodies existence and bliss.
When combined, Shiva becomes the ever-auspicious presence, the one who transcends life and death, form and formlessness.
Shiva is not merely a god, but a state of consciousness—the unmanifest reality, the silent awareness behind all experiences. As a God, Lord Shiva is known as Mahadeva, Nataraja, Rudra, Ardhanarishwara, Adi Yogi, or Pasupati. Shiva is known as the destroyer of ignorance.
Guruji, Sri Amit Ray once said:
"Within the divine flow of energies in the body, the 72,000 Nadis are like rivers—each flowing from the sacred source of Shiva’s matted locks, where Ganga descends and the moon drinks immortality." - Sri Amit Ray
Who is Shiva in Hinduism and the Puranas?
In Hinduism, Shiva is one of the most revered deities, forming part of the Trimurti—the cosmic trinity of Brahma (creator), Vishnu (preserver), and Shiva (destroyer or transformer). However, Shiva is not limited to destruction; he is also known as the Supreme Consciousness, the inner Self, and the Adi Yogi (first yogi).
In the Puranas, especially the Shiva Purana, Linga Purana, and Skanda Purana, Shiva is depicted in many forms:
- As Mahadeva – the Great God.
- As Nataraja – the Lord of the Cosmic Dance.
- As Ardhanarishwara – half-man, half-woman (union of Shiva and Shakti).
- As Pashupati – Lord of all beings.
- As Rudra – the fierce and primal storm deity from the Rigveda, later absorbed into Shiva.
✨ Key Attributes in the Puranas:
- He resides in Mount Kailash, meditating in eternal stillness.
- He wears ashes, symbolizing renunciation and ego-destruction.
- The river Ganga flows from his hair, representing divine knowledge.
- The moon on his head signifies time and transcendence.
The Shiva Linga, often misunderstood, symbolizes formless consciousness and the union of Shiva and Shakti—not just a physical object but a sacred energy symbol. The 72,000 Nadis are the sacred rivers climbing toward the divine—fed by the waters of Ganga, rooted in Shiva’s crown, and blossoming under the moon of serene wisdom

☑️

☑️

☑️

☑️

☑️

☑️

☑️
🔱 The Layers of Shiva’s Meaning
1. Shiva as the Supreme Consciousness
In yogic philosophy, Shiva represents pure awareness (Purusha)—that which observes all but remains unchanged. This aspect is often paired with Shakti, the creative energy or dynamic aspect of reality.
2. Shiva as the Destroyer of Ignorance
In the Hindu Trinity (Trimurti), Shiva is known as the destroyer, but this does not mean evil—it means he dismantles illusion, ego, and ignorance (Avidya), paving the way for rebirth and liberation (moksha).
3. Shiva as the Yogi and the Adi Guru
Shiva is also the first yogi (Adi Yogi) and the first teacher (Adi Guru) who gave the science of yoga, tantra, and meditation to the Saptarishis. As a meditating ascetic, Shiva symbolizes mastery over mind and senses.
4. Shiva as Ardhanarishwara (Wholeness of Duality)
The form of Ardhanarishwara, half Shiva and half Shakti, reminds us that divine consciousness is neither masculine nor feminine—but a perfect union of both.
🕉️ Shiva’s Symbols and Their Meanings
| Symbol | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Trishula (Trident) | Mastery over creation, preservation, and destruction |
| Third Eye | Spiritual wisdom, inner vision, transcendence of duality |
| Crescent Moon | Time cycles, eternity, calm in chaos |
| River Ganga | Purification and divine knowledge |
| Ash-covered Body | Renunciation of ego and attachment |
| Serpent around Neck | Control over fear, death, and desires |
| Damru (Drum) | Vibration of creation and dissolution—Om |
🧘 Shiva in Meditation and Spiritual Practice
- Mantra: The sacred sound “Om Namah Shivaya” means “I bow to the inner Self, to Shiva.” "Om Namah Shivaya" is one of the most respected mantras of the world. You can learn the Five Great Shiva Mantras.
- Meditation: Shiva is the stillness behind all movement. Meditating on Shiva leads to inner silence, awakening of the third eye, and dissolving of the ego-self.
- Shiva in Tantra: He represents the unmoving consciousness, the still witness to the dance of Shakti (energy, life, emotion).
🔑 Key Takeaways
- Shiva means “The Auspicious One” and symbolizes pure, eternal consciousness.
- He is the destroyer of illusion, ego, and false identity—not of life, but of ignorance.
- Lord Shiva is known as Mahadev, Nataraja, Rudra, Ardhanarishwara, Pasupati.
- Shiva represents the state of spiritual liberation, stillness, and unity with the universe.
- As Adi Yogi, Shiva gave us yoga, breath, silence, and wisdom to walk the inner path.
- Meditating on Shiva leads to clarity, detachment, freedom, and bliss.
🙏 Why Understanding Shiva Matters Today
In a world full of noise, chaos, and superficial identity, Shiva invites us back to silence, depth, and truth. He teaches us not to suppress or escape reality but to see through it with clarity. When you understand Shiva, you no longer fear endings—because you realize that every ending is a doorway to rebirth and expansion.
❓FAQs About Shiva Meaning
Q1: Is Shiva a god or a force?
Both. In mythology, he is worshipped as a deity. But in yogic philosophy, Shiva is the unchanging awareness, the infinite field of consciousness beyond time and form.
Q2: What is Shiva consciousness?
It is a state of pure, meditative stillness—free from ego, thought, and identification. It is being fully aware yet untouched.
Q3: Why is Shiva called the destroyer?
He destroys illusion, falsehood, and attachment—so that truth, freedom, and light can emerge.
Q4: What is the meaning of “Om Namah Shivaya”?
It means “I bow to the Supreme Self within”—honoring Shiva not just as a god, but as the divine presence inside you.
Q5: How do I connect with Shiva spiritually?
Through mantra chanting, meditation, self-inquiry, and living with awareness, you can align with Shiva consciousness.
Read more ..
The Soleus Pushup Exercises: Benefits and the Techniques
The soleus muscle is an often-overlooked muscle in the lower leg that is responsible for plantarflexion of the ankle, which is the action of pointing the foot downward. While it may not be as well-known as other leg muscles, the soleus plays a crucial role in a variety of activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
One effective exercise for targeting the soleus muscle is the soleus pushup. This exercise involves lifting the heel while keeping the front of the foot stable, which is the opposite of a traditional calf raise where the heel remains on the ground.
In this article, you will explore the benefits of the soleus pushup exercises and how to properly perform the exercise, with tips and techniques.
Recent findings published in the scientific journal iScience [1] have suggested that incorporating soleus pushups into your exercise routine may have several health benefits. The soleus pushup exercise targets the soleus muscle located in the calf and can lead to an increased metabolic rate, lower blood sugar levels, and reduced risk for type 2 diabetes.
Read more ..
Managing Anger: Guidelines for Controlling Your Emotions
Managing anger is an important aspect of maintaining healthy relationships and promoting overall well-being. By recognizing the signs of anger, identifying the underlying causes, and utilizing evidence-based strategies such as relaxation techniques, assertive communication, and therapy, individuals can learn to control their emotions and reduce the negative impact of anger on their lives.
Fortunately, there are many strategies and techniques that can help us manage our anger and control our emotions. In this article, you will explore five guidelines for managing anger and regaining control over our emotions.
What is Anger?
Anger is an emotion that we all experience from time to time. It can be a useful and necessary emotion, helping us to express our feelings and communicate our needs. However, when anger becomes out of control, it can lead to destructive behavior and damage our relationships with others.
Anger is a complex emotion that involves a variety of neural pathways and physiological responses. At its core, anger is thought to be related to the brain's "fight or flight" response, which is activated in response to perceived threats or challenges. The amygdala, a small almond-shaped structure in the brain's limbic system, is thought to play a central role in the experience of anger. Anger is a complex emotional state that can range in intensity from mild annoyance to intense fury and rage [1]. During angry recollections, the amygdala fired. At the same time, a part of the orbital frontal cortex, just above the eyes, also engaged, putting control on your emotions [2].
Read more ..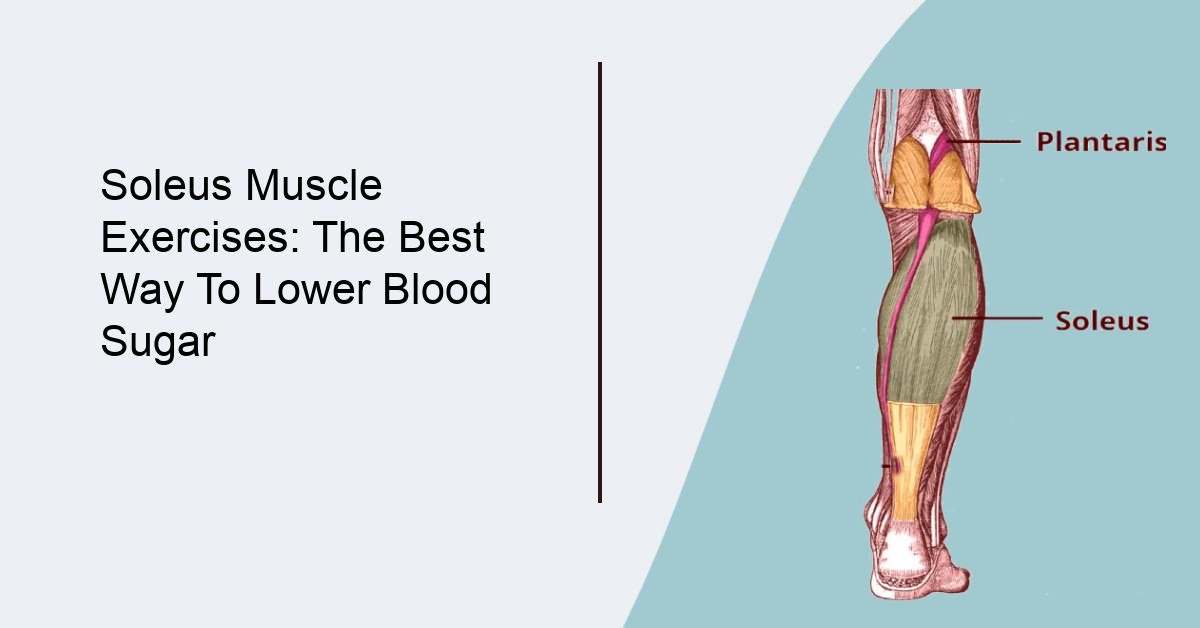
Soleus Muscle Exercises: The Best Way To Lower Blood Sugar
The soleus muscle is a powerful muscle located in the back of the lower leg, just beneath the calf muscles. It is responsible for maintaining posture, balance, and stability during physical activities such as standing and walking. Recent studies have found that exercises that specifically target the soleus muscle can be highly effective in reducing blood sugar levels in people with diabetes.
In this article, we will explore the role of the soleus muscle in blood sugar regulation, the benefits of soleus muscle exercises, and some examples of soleus muscle exercises that can help lower blood sugar.
Role of the Soleus Muscle in Blood Sugar Regulation
The soleus muscle is an important regulator of blood sugar levels because it contains a high concentration of glucose transporters, which are responsible for transporting glucose from the bloodstream into the muscle cells where it can be used for energy. In people with diabetes, this process is impaired, resulting in elevated blood sugar levels.
Read more ..
Nitric Oxide Dump Exercises - The Best Way to Lower Blood Pressure
Do you know Nitric Oxide Dump exercises can lower your blood pressure? It only needs four minutes to complete. The Nitric Oxide Dump exercise consists of squats and arm raises, circular arm swings, and shoulder presses. The nitric oxide dump or nitric oxide blowout takes only four minutes. By practicing all of these exercises, you maximize the amount of blood flow throughout your body, rather than limiting it to just one portion of your body.
High blood pressure or hypertension is a common health problem that affects millions of people around the world. It is a silent killer that can cause serious health issues if left untreated. One of the best ways to lower blood pressure is through exercises. However, not all exercises are equal, and some can be harmful to people with hypertension. That is where nitric oxide dump exercises come in.
In this article, we will explore what nitric oxide dump exercises are, their benefits, how to perform them, and the modern research on it.
What are Nitric Oxide Dump Exercises?
Nitric oxide dump exercises are a form of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) that aims to boost the production of nitric oxide in the body. Nitric oxide is a gas that helps to relax and dilate blood vessels, which in turn, helps to lower blood pressure. The idea behind nitric oxide dump exercises is to perform short bursts of high-intensity exercises that increase the production of nitric oxide in the body.
Read more ..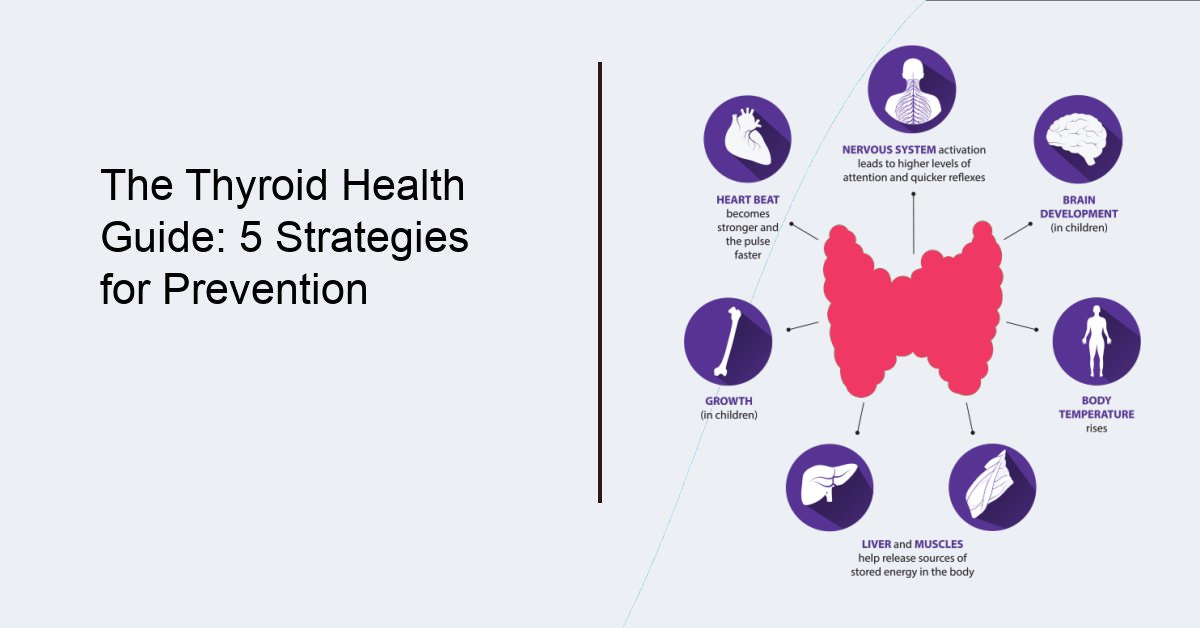
The Thyroid Health Guide: 5 Strategies for Prevention
The thyroid gland, located in the neck, is responsible for producing hormones that regulate metabolism and energy levels in the body. When the thyroid gland produces too much or too little of these hormones, it can lead to various health problems. Thyroid disorders are more common in women than men, and the risk increases with age. However, there are several thyroid prevention strategies that can be implemented to maintain a healthy thyroid gland.
In this article, you will learn five thyroid prevention strategies, the symptoms of thyroid disorders, the best diet plans, and other important considerations.
What is Thyroid?
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below the Adam's apple. It is an essential part of the endocrine system, which is responsible for producing and regulating hormones in the body. The thyroid gland produces two main hormones, triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4), which play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development. The thyroid gland is also responsible for producing calcitonin, a hormone that helps regulate calcium levels in the body. When the thyroid gland is not functioning properly, it can lead to a variety of health problems, including thyroid disorders [1].
What are Thyroid Hormones?
Thyroid hormones are hormones produced by the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck. The two main thyroid hormones are triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4). These hormones play a crucial role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development in the body.
T4 is the most abundant thyroid hormone and is often considered the "storage" form of thyroid hormone because it is converted to T3, the more active form of the hormone, in the liver and other tissues. T3 is considered the "active" form of thyroid hormone because it is responsible for the majority of the metabolic effects of thyroid hormone in the body.
Thyroid hormones are involved in a wide range of processes in the body, including:
- Regulating metabolism and energy production
- Supporting growth and development
- Regulating body temperature
- Maintaining heart rate and blood pressure
- Regulating the digestive system
- Supporting bone health and calcium balance
When the thyroid gland is not functioning properly and producing too much or too little thyroid hormone, it can lead to a variety of health problems, including thyroid disorders.
Read more ..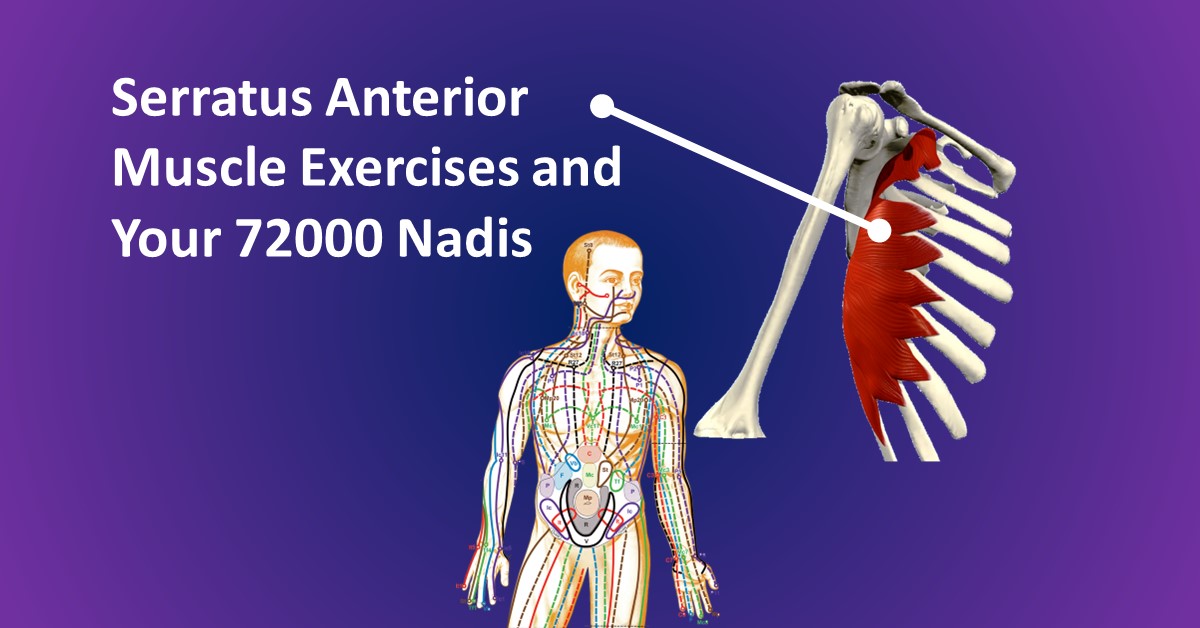
Serratus Anterior Muscle Exercises and Your 72000 Nadis
The serratus anterior muscle exercises are often powerful in removing various types of blockages from the chakras and the energy bodies. It plays a pivotal role not just in physical activities but also in promoting chakra balancing and removing Nadi-related energy blockages in the mind-body system.
In this article, we explore the world of serratus anterior, exploring breathing techniques, stretching exercises, benefits, and crucial precautions to ensure a harmonious integration into your spiritual, mental, and physical well-being.

In the Sri Amit Ray traditions of the Ray Advanced Kriya Yoga system, like the soleus muscle, Serratus Anterior Muscle, the levator scapulae muscle has many subtle kriyas.
Serratus Anterior Muscle
The serratus anterior is a fan-shaped muscle located on the lateral aspect of the rib cage. It originates from the surface of the upper eight or nine ribs and inserts into the anterior surface of the medial border of the scapula (shoulder blade). In some traditions of ancient yoga, it is considered that the serratus anterior muscle alignment holds the key to eternal youth. While traditionally associated with pushing movements, unlocking its potential as a breathing muscle can bring about a host of benefits.
Serratus Anterior Muscle and Your Chakras and Nadis
In 2005, His Holiness Sri Amit Ray discovered the 114 chakras to understand the total neuropsychology, human mind, body, and spiritual energy the body experiences. He introduces the names, locations, functions, mantras, and techniques for awakening of the 114 chakras. Among the 114 chakras, a set of chakras is associated with the serratus anterior muscles. Similarly, a group of energy channels (Nadis) are associated with the serratus anterior muscles. The concept of 114 chakras offers a unique and innovative perspective on the understanding of the body-mind-consciousness energy centers in the human body.
Each of these chakras could have specific functions, including the regulation of emotions, the facilitation of physical well-being, and the enhancement of spiritual awareness. In the tradition of the 72000 Nadis System originated by Sri Amit Ray, exercises that focus on the serratus anterior are vital for balancing the Ida and Pingala and activating the Sushumna Nadi in the spine.
Nadis are subtle energy channels that crisscross the body, carrying the life force known as Prana. It is believed that there are 72,000 Nadis forming an intricate network, influencing physical, mental, and spiritual well-being. The activation and harmonization of these Nadis are central to practices like Yoga and Ayurveda.
The serratus anterior, through its engagement and release during specific exercises, may influence the flow of Prana through the Nadis. As the muscle contracts and relaxes, it creates a dynamic energy exchange, potentially enhancing the vitality of these energy channels. In the Sri Amit Ray traditions of yoga suggest that a balanced and free-flowing life force (Prana) contributes to overall health, heightened awareness, emotional stability, and total spiritual growth.
Serratus Anterior Muscle Exercises
The serratus anterior exercises include shoulder extension, forward punch, serratus anterior punch, dynamic hug, scaption (with external rotation), press-up, push-up plus, and knee push-up plus [1]. Rowing exercises have been recommended for strengthening the trapezius muscle [2]. The standard push-up plus provides a dynamic way to target and strengthen the serratus anterior muscles, contributing to improved shoulder function and overall upper body strength [3].
Read more ..
Cosmic Energy Healing Meditation
How can one enter a state of profound healing and deep meditation? The important thing is to maintain the correct cosmic connection and the appropriate attitude while you are practicing. These are the kinds of things that have a significant impact.
When you open yourself up to the cosmic nadis and the cosmic energy, you'll be able to let go of harmful habits and toxins as well as emotional baggage, allowing you to come into greater harmony with your true self.
His Holiness Sri Guru Amit Ray, in his Himalayan deep meditations around 2005, rediscovered the full framework of all 72,000 Nadis.
How do you meditate in a significant way?
Before beginning the practice, make sure you have a thorough preparation, also known as a "deep relaxation." This involves completely relaxing the body, engaging in a few rounds of deep breathing, cultivating a pleasant mental state, and having the intent to delve deeply into your meditation practise.

What does meditation feel like?
It also depends on how deeply you are able to delve into the subject matter, as various methods impart a distinct "feel" to the experience. On the other hand, there is a pervasive sense of being totally at ease while also being centered and focused. You experience a sense of fulfilment, clarity, and awareness in the here and now.
Read more ..
Sushumna Nadi Activation - The Spinal Energy Channel Activation
There are 72000 nadis in human body, and the Sushumna Nadi is very important. The ida nadi is located on the left side of the body, the sushumna nadi is located in the centre, and the pingala nadi is located on the right side of the body. All three of these nadis run from the base of the spine to the head. The ultimate objective is to clear these nadis of obstructions in order to achieve perfect relaxation, healing, freedom from toxic thoughts, and perfect creativity.
The Shiva Samhita states that 350,000 nadis emerge from the centre of the navel, while the Katha Upanishad (6.16) mentions 101 channels radiating from the heart. Traditional yoga texts such as the Hatha Yoga Pradipika and Goraksha Samhita mention 72,000 nadis.
During a period of deep meditation in the Himalayan foothills around the year 2005, His Holiness Sri Guru Amit Ray rediscovered the complete framework of all 72000 Nadis. Many of these Nadis are associated with the Cosmic Energy Meditation.
In 2005, for activating the Sushumna Nadi Ray discovered a special type of yoga kriya, which is known as Ray Mayur Sanchalan Kriya.
The origin of the 114 chakras can be traced back to Sri Amit Ray's long introspective contemplation in the Himalaya. As Sri Amit Ray was engaged in prolonged spiritual fasting and deep meditation in 2005, he had a vision of the 114 Chakars and their relations with the 72000 Nadis.
During deep meditation, when the air no longer flows through the nose, the Prana or the Life-force moves through Sushumna energy channel, and the mind gradually merges with the Life-force and begins to move together.
Ray Mayur Sanchalan Kriya:
In 2005, Sri Guru Amit Ray discovered a special type of yoga kriya known as the Ray Mayur Sanchalan Kriya for activating the Sushumna Nadi. Here, Mayur Sanchalan means opening the feathers (nadis) like a peacock. This is a set of exercises and meditation practices. It activates many subtle energy channels in the body, along with the Sushumna Nadi.
Read more ..